Arithmetic can be divided into some special purpose integer predicates and a series of general predicates for floating point and integer arithmetic as appropriate. The integer predicates are as ``logical'' as possible. Their usage is recommended whenever applicable, resulting in faster and more ``logical'' programs.
The general arithmic predicates are optionaly compiled now (see please/3 and the -O command line option). Compiled arithmetic reduces global stack requirements and improves performance. Unfortunately compiled arithmetic cannot be traced, which is why it is optional.
The general arithmetic predicates all handle expressions. An
expression is either a simple number or a function. The arguments
of a function are expressions. The functions are described in
section ![]() .
.
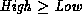 . If
Value is an integer,
. If
Value is an integer, 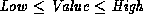 .
When Value is a variable it is successively bound to all
integers between Low and High.
.
When Value is a variable it is successively bound to all
integers between Low and High.
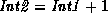 . At least one of the arguments
must be instantiated to an integer.
. At least one of the arguments
must be instantiated to an integer.
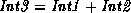 . At least two of the
three arguments must be instantiated to integers.
. At least two of the
three arguments must be instantiated to integers.
> +Expr2
< +Expr2
=< +Expr2
>= +Expr2
=\= +Expr2
=:= +Expr2