Here we prove Bayes Rule from probability calculus. P(A) denotes the probability that event A will occur. Belief measure obeys the three basic axioms of probability theory:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The proof derives from the multiplication rule of probability theory which is:
![]()
Then:
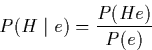
By swapping He and using the multiplication rule again:
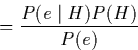
qed.